Blood Sugar Control: Your Guide to Balanced Glucose Levels
When managing blood sugar control, the practice of keeping blood glucose within a target range to support overall health. Also known as glycemic management, it plays a central role in preventing short‑term spikes and long‑term complications. Your pancreas releases hormones, you eat carbs, and the rest of your body reacts—all in a few minutes. If the balance tilts, you might feel shaky, tired, or notice frequent urination. Over years, uncontrolled levels can damage nerves, kidneys, eyes, and the heart. That’s why understanding the moving parts behind blood sugar control matters for anyone, whether you’ve been diagnosed with a condition or simply want to stay energetic.
One of the most powerful players is Insulin, a hormone that lowers blood glucose by helping cells absorb sugar. When insulin works properly, it acts like a key that opens doors on muscle and fat cells, allowing glucose to flow in for energy or storage. If those doors jam, blood sugar stays high—what doctors call hyperglycemia. The opposite problem, too little insulin, leads to low blood sugar or hypoglycemia, which can cause dizziness or even loss of consciousness. Another central piece is Diabetes, a chronic condition where blood sugar regulation is impaired. Type 1 diabetes means the body stops making insulin, while Type 2 often involves insulin resistance, where cells ignore the hormone’s signal. Both types demand careful monitoring, lifestyle tweaks, and sometimes medication.
Food choices are guided by the Glycemic Index, a ranking of foods based on how quickly they raise blood glucose. Low‑GI foods—like oats, legumes, and most fruits—release glucose slowly, helping you avoid sudden spikes. Pairing carbs with protein or healthy fats further smooths the curve. Technology has made monitoring easier than ever. A Continuous Glucose Monitor, a device that provides real‑time glucose readings throughout the day can alert you before you hit dangerous lows or highs, letting you adjust insulin doses or snack choices on the fly. Together, these tools create a feedback loop: diet influences glucose, glucose data informs insulin, and insulin levels shape future dietary decisions. Mastering this loop is the heart of effective blood sugar control.
Putting It All Together
Start by checking your baseline—fasting glucose or an HbA1c test gives you a snapshot of where you stand. Then choose a monitoring method that fits your lifestyle, whether a simple finger‑stick meter or a CGM. Build meals around low‑GI ingredients, add protein and fiber, and stay active; even a short walk after meals can boost insulin sensitivity. If you’re on medication, keep a log of doses, meals, and readings to spot patterns. The articles below dive deeper into each of these pieces, from detailed drug comparisons to lifestyle hacks, giving you a toolbox to tighten your glucose game and stay on top of your health.
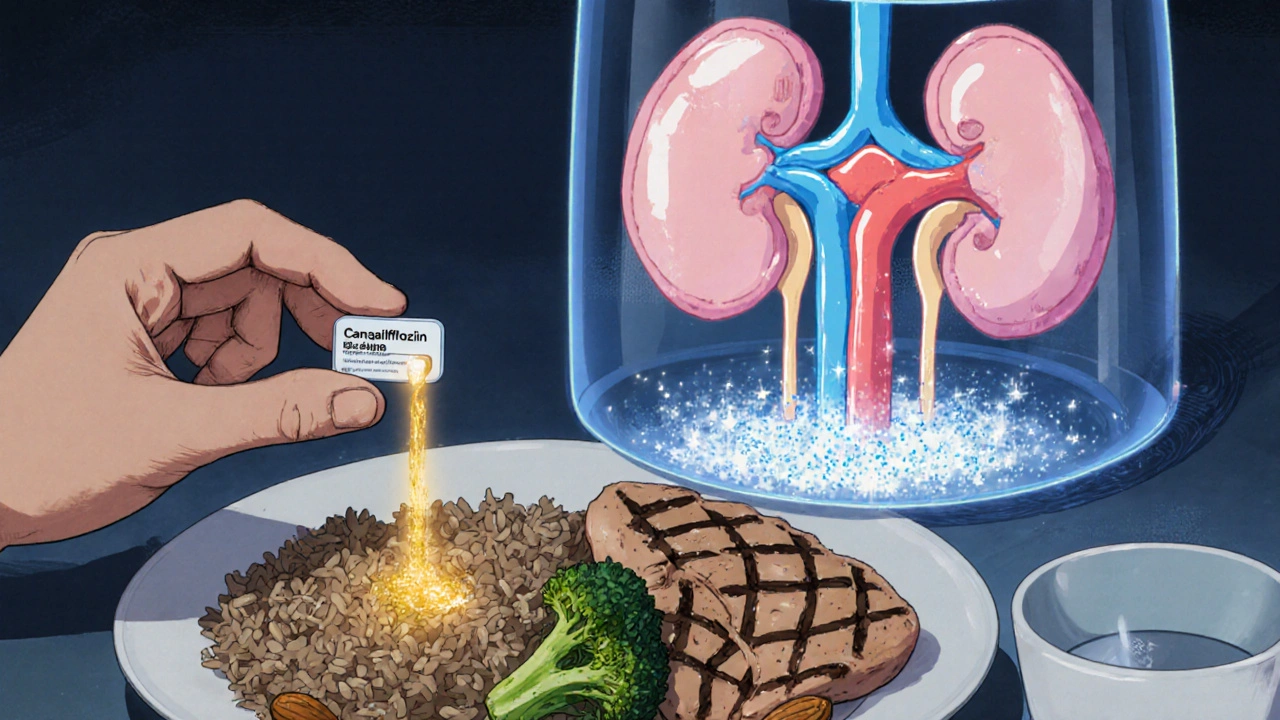
Canagliflozin and Lifestyle Changes: How to Make the Most of Your Treatment Plan
Canagliflozin works best when paired with simple, daily lifestyle changes. Learn how diet, movement, sleep, and hydration boost its effectiveness for better blood sugar control in type 2 diabetes.
How Saxagliptin Improves Quality of Life for Diabetes Patients
Learn how Saxagliptin works, its benefits, safety tips, and real‑world advice to boost quality of life for people with Type 2 diabetes.
Diabetes Management: Top Lifestyle Tips for Better Blood Sugar
Practical lifestyle tips for diabetes management covering diet, exercise, monitoring, and daily habits to keep blood sugar stable.